Female Reproductive Anatomy
The reproductive system is the part of the body involved in sexual function. In women, this system is also responsible for nourishing and supporting a baby as it develops. Below are the main parts of the female reproductive anatomy.
A doctor that specializes in caring for a woman's reproductive system is called a gynecologist.
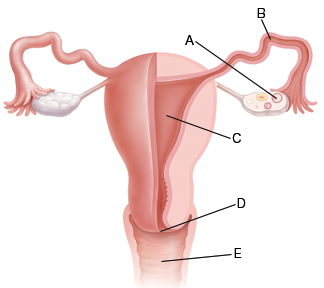 Front View
Front View
A. Ovaries store eggs (female reproductive cells). About once a month, an egg is released from an ovary. This is called ovulation.
B. Fallopian tubes carry eggs to the uterus. Pregnancy occurs if a man's sperm fertilizes an egg as it moves through the tube.
C. The uterus is a hollow, muscular, pear-shaped organ. If an egg has been fertilized, the embryo implants in the lining of the uterus where it grows into a baby.
D. The cervix is the narrow canal where the uterus and vagina meet.
E. The vagina is the pathway that connects the uterus with the outside of the body.
During ovulation, the lining of the uterus thickens. This helps prepare the uterus to receive and nourish a fertilized egg. If pregnancy doesn't occur, the thickened lining is no longer needed. It is then shed through the vagina as menstrual bleeding (having a period).
Publication Source: National Cancer Institute
Online Source: National Cancer Institute
Date Last Reviewed: 2007-01-15T00:00:00-07:00
Date Last Modified: 2005-07-29T00:00:00-06:00